10 changed files with 51 additions and 27 deletions
BIN
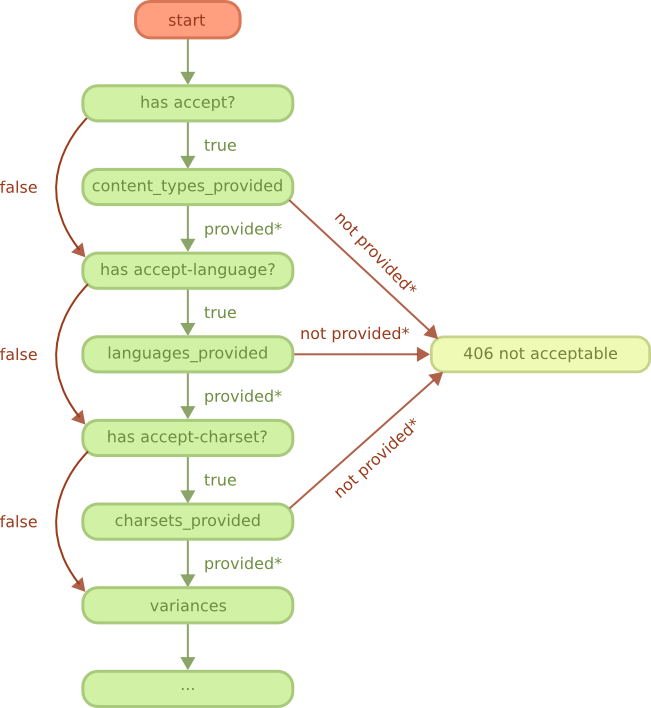
guide/rest_cond.png

BIN
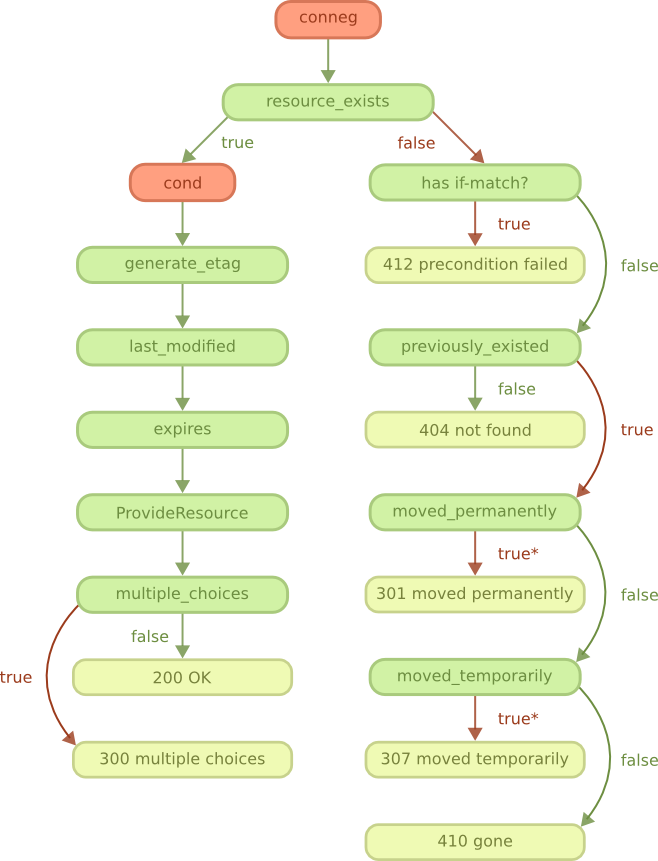
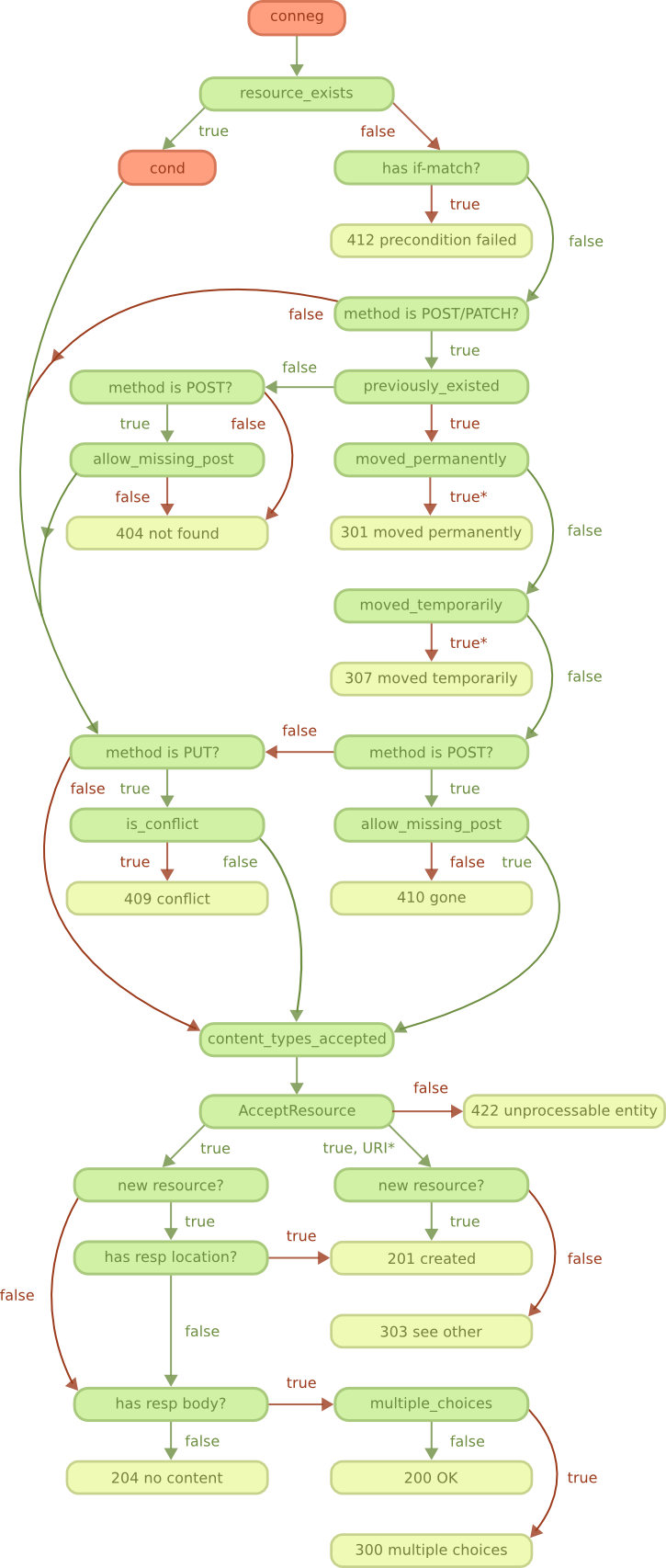
guide/rest_conneg.png
BIN
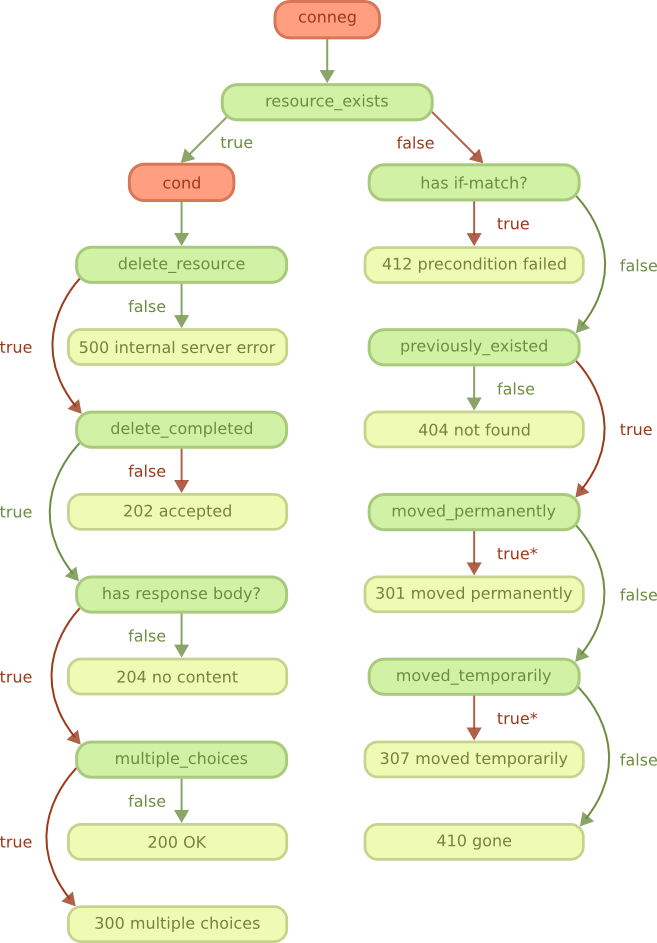
guide/rest_delete.png
+ 42
- 0
guide/rest_flowcharts.md
|
|||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
BIN
guide/rest_get_head.png
+ 8
- 22
guide/rest_handlers.md
|
|||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
BIN
guide/rest_options.png
BIN
guide/rest_put_post_patch.png
BIN
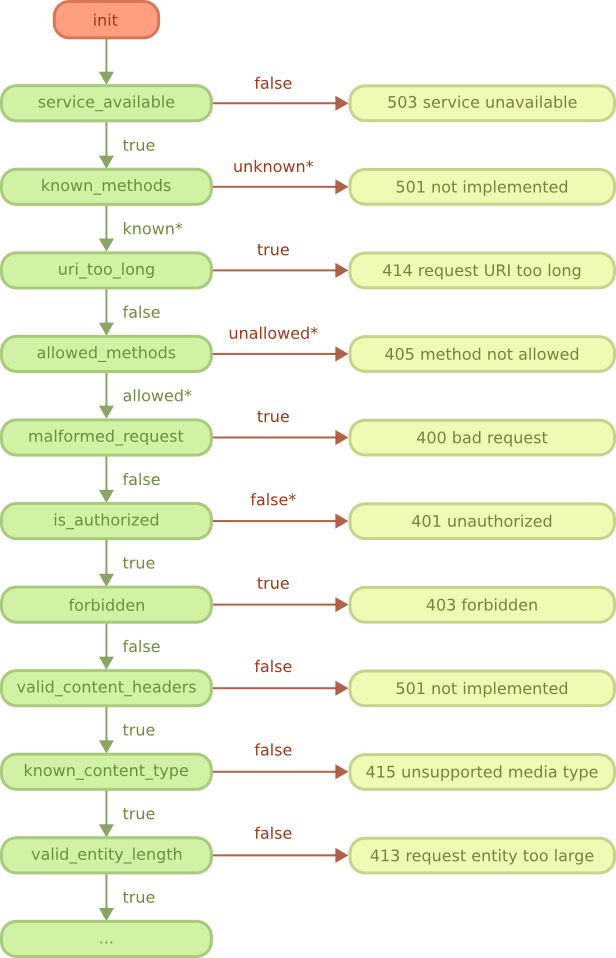
guide/rest_start.png
+ 1
- 5
guide/toc.md
|
|||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||